Loading
Heroin (Gear/Smack/Scag/Horse/Brown)
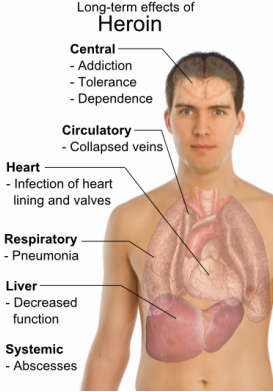
There are plenty of names for this substance, but diamorphine, to give it it's correct medical name was originally manufactured in 1898 by the German pharmaceutical company, Bayer. It was given the brand name "heroin" from the Greek "Heros" as it was said to make the user feel heroic, and was marketed as a cough medicine, general pain killer, a cure for morphine addiction and an anaesthetic to send babies with colic to sleep. By 1920, New York had approximately 300 000 heroin addicts.
In the UK, there were relatively few heroin addicts until it was made illegal in 1968. The criminalisation of heroin meant doctors weren't allowed to prescribe it and began prescribing methadone, a bright green liquid which some claim is more dangerous, instead. In fact, many users simply sell their methadone for heroin as methadone counters the effects of cold turkey to some degree depending on the size of the user's dose- "monkey". The quality of heroin suffered, as the gangsters and smugglers filled the void, and what we now know as "brown" became the main form. This is mixed with lemon juice and cooked on a spoon until it is dissolved. It is then sucked up into a syringe (works) through a cigarette filter and injected (dug). For a heroin user, methadone does not give the high of heroin. It only counters the side effects. Some claim it only does this to a certain degree. In recent years, doctors have begun prescribing buprenorphine, a pain killer which comes in tablet form under names such as suboxone and subutex. These are often crushed and snorted or injected, though in the case of suboxone, injecting negates it's opiate effect. Buprenorphine in any form is believed to be less addictive than methadone but has been linked to respiratory problems in users.
Not many heroin users begin by injecting. Far more common is "chasing the dragon", which involves heating the drug on foil and inhaling the smoke. Some also chop it into lines and snort it like cocaine, or smoke it in glass pipes.
It is almost unheard of to see 100% pure heroin, particularly on the streets. Even a long term heroin addict would be killed by even a small dose of pure heroin. This is the result of criminalisation. In the past, a heroin addict would only have the worry of overdosing. Since the law drove it underground, the mixture of a horrendous variety of additives such as detergent, ground glass, battery acid, brick dust and powdered animal faeces just to name a few, have resulted in the user being lucky if their fix is 10% pure. The complications that are prominent in addicts, such as hepatitis, septicaemia and thrombosis are generally down to the additives and the sharing of needles that is prevalent amongst users, also increasing the risks of HIV and AIDS.
Heroin gives the user an intensely warm and comfortable sensation. The experience is difficult to describe but users claim is the best high in the world. As it is a depressant, it relaxes the user and gives a euphoric meditative feeling that they are indifferent to anything. The duration of this can vary depending on the amount taken and the purity of the hit. Injecting is said to said to make the sensation more intense, and users tend to flush back, suck blood into the syringe so it mixes with the drug and makes the hit even harder. Some, however, say there is no evidence that it makes any difference. Many first time users will retch or vomit whichever way they use the drug.
Heroin causes the user to become constipated, resulting in diarrhoea being one of the side effects of withdrawal, highlighted in the memorable toilet scene in the film "Trainspotting". Other withdrawal symptoms, include extreme fever, nausea, cramp, sweats, insomnia and more. As Ewan McGregor's character in Trainspotting says, "Imagine the worse flu you've ever had, multiply it by 100 and you're nowhere near half of what it feels like." Or words to that effect. The good news is that the withdrawal symptoms- "cold turkey", despite making the victim feel terrible, even suicidal, the user will not die from the effects, though they may well feel like it when it's happening. This is the opposite of alcohol withdrawal, where the rapid body temperature change will kill the user. The brain cells that heroin destroys will regenerate, unlike those damaged by alcohol.
One of the more unpleasant side effects of injecting heroin long term is the collapsing of the user's veins. With heavy use and regular injecting, the user is often unable to find a vein strong enough to inject into, which results in the injecting into the eye or groin. Thrombosis is common in long term needle users.
Speedballing-injecting heroin and cocaine together, or moonrock, smoking the two together, are common practices among users. As one is an upper and the other a downer, the two hit at the same time with the two drugs dumbing down the negative effects, for example, the paranoia that is sometimes felt by heroin users while on the drug. This puts added strain on the cardiovascular system in particular and increases the risk of cardiac arrest.
Heroin is highly addictive because the user has to take enough to counteract the effects of cold turkey. Tolerance builds up quickly. so the user needs more to achieve the same high as previously. This means constantly increasing the dose as the body adapts. The more the user takes, the more expensive it becomes, which often leads to crime. Many prostitutes are reliant on people who keep them under control by means of heroin.
A true drug addict will do anything to get their fix. At the same time, the stereotype junkie potrayed in the media is not particularly accurate. Some say moderate use can make users appear younger looking as opposed to older. Many users often lead normal lives on a stable dose. The distinction has to be made between the drug user and the addict. Heroin can VERY easily become a lifestyle.
In the UK, there were relatively few heroin addicts until it was made illegal in 1968. The criminalisation of heroin meant doctors weren't allowed to prescribe it and began prescribing methadone, a bright green liquid which some claim is more dangerous, instead. In fact, many users simply sell their methadone for heroin as methadone counters the effects of cold turkey to some degree depending on the size of the user's dose- "monkey". The quality of heroin suffered, as the gangsters and smugglers filled the void, and what we now know as "brown" became the main form. This is mixed with lemon juice and cooked on a spoon until it is dissolved. It is then sucked up into a syringe (works) through a cigarette filter and injected (dug). For a heroin user, methadone does not give the high of heroin. It only counters the side effects. Some claim it only does this to a certain degree. In recent years, doctors have begun prescribing buprenorphine, a pain killer which comes in tablet form under names such as suboxone and subutex. These are often crushed and snorted or injected, though in the case of suboxone, injecting negates it's opiate effect. Buprenorphine in any form is believed to be less addictive than methadone but has been linked to respiratory problems in users.
Not many heroin users begin by injecting. Far more common is "chasing the dragon", which involves heating the drug on foil and inhaling the smoke. Some also chop it into lines and snort it like cocaine, or smoke it in glass pipes.
It is almost unheard of to see 100% pure heroin, particularly on the streets. Even a long term heroin addict would be killed by even a small dose of pure heroin. This is the result of criminalisation. In the past, a heroin addict would only have the worry of overdosing. Since the law drove it underground, the mixture of a horrendous variety of additives such as detergent, ground glass, battery acid, brick dust and powdered animal faeces just to name a few, have resulted in the user being lucky if their fix is 10% pure. The complications that are prominent in addicts, such as hepatitis, septicaemia and thrombosis are generally down to the additives and the sharing of needles that is prevalent amongst users, also increasing the risks of HIV and AIDS.
Heroin gives the user an intensely warm and comfortable sensation. The experience is difficult to describe but users claim is the best high in the world. As it is a depressant, it relaxes the user and gives a euphoric meditative feeling that they are indifferent to anything. The duration of this can vary depending on the amount taken and the purity of the hit. Injecting is said to said to make the sensation more intense, and users tend to flush back, suck blood into the syringe so it mixes with the drug and makes the hit even harder. Some, however, say there is no evidence that it makes any difference. Many first time users will retch or vomit whichever way they use the drug.
Heroin causes the user to become constipated, resulting in diarrhoea being one of the side effects of withdrawal, highlighted in the memorable toilet scene in the film "Trainspotting". Other withdrawal symptoms, include extreme fever, nausea, cramp, sweats, insomnia and more. As Ewan McGregor's character in Trainspotting says, "Imagine the worse flu you've ever had, multiply it by 100 and you're nowhere near half of what it feels like." Or words to that effect. The good news is that the withdrawal symptoms- "cold turkey", despite making the victim feel terrible, even suicidal, the user will not die from the effects, though they may well feel like it when it's happening. This is the opposite of alcohol withdrawal, where the rapid body temperature change will kill the user. The brain cells that heroin destroys will regenerate, unlike those damaged by alcohol.
One of the more unpleasant side effects of injecting heroin long term is the collapsing of the user's veins. With heavy use and regular injecting, the user is often unable to find a vein strong enough to inject into, which results in the injecting into the eye or groin. Thrombosis is common in long term needle users.
Speedballing-injecting heroin and cocaine together, or moonrock, smoking the two together, are common practices among users. As one is an upper and the other a downer, the two hit at the same time with the two drugs dumbing down the negative effects, for example, the paranoia that is sometimes felt by heroin users while on the drug. This puts added strain on the cardiovascular system in particular and increases the risk of cardiac arrest.
Heroin is highly addictive because the user has to take enough to counteract the effects of cold turkey. Tolerance builds up quickly. so the user needs more to achieve the same high as previously. This means constantly increasing the dose as the body adapts. The more the user takes, the more expensive it becomes, which often leads to crime. Many prostitutes are reliant on people who keep them under control by means of heroin.
A true drug addict will do anything to get their fix. At the same time, the stereotype junkie potrayed in the media is not particularly accurate. Some say moderate use can make users appear younger looking as opposed to older. Many users often lead normal lives on a stable dose. The distinction has to be made between the drug user and the addict. Heroin can VERY easily become a lifestyle.
Opium (Hop, Midnight Oil)

Heroin is an opiate, meaning it is a derivative of opium. Pure opium contains morphine, which is the processed part of the plant for medical and illegal use, as well as codeine and other opiates that are processed for narcotic use.
As heroin is easier to smuggle, being less dense, pure opium is rare in the Western world. To many people it has a romantic and exotic image. So much so that there is a perfume named after it.
During the 1840s, British warships shelled several Chinese ports for the right to import opium from India to China. The Opium Wars again broke out in the late 1850s. These wars gave the English language the expression "gunboat diplomacy" and secured Hong Kong as a British colony until 1997. Indeed, the import and export of opium was crucial to the British economy until its prohibition in the early 20th century.
Opium can be injected, but most popularly smoked in pipes or chased on foil like heroin. Its use goes back to Ancient times and is mentioned in texts from the Babylonians, Phoenicians, Assyrians, Greeks, Egyptians and Romans and traded throughout the Mediterranean and known Ancient world.
Its use was also widespread throughout the Islamic world. This caused its stigmatization by the Spanish Inquisition as a non-Christian influence, and it fell from favour until Paracelsus developed laudanum in the 16th Century. Laudanum is a "tincture" of opium disolved in alcohol and used as a painkiller/anaesthetic. Laudanum was widely used in Victorian times-indeed the Queen herself is rumoured to have used it.
Opium has a wide and colourful history, but in modern times the majority of opium is mainly cultivated in the Indo-Chinese world, as well as Afghanistan and South East Asia. Opium poppies however, can be grown all over the world.
The most famous literary reference to opium is the classic "Confessions Of An English Opium Eater" by Thomas De Quincey. The poet Coleridge was a well known user, as was Alfred Lord Tennyson. Horatio Nelson is probably the most famous opium addict, which began when he was given it as a pain killer after his arm was amputated. Other notable addicts included anti-slavery campaigner William Wilberforce and Clive of India. Towards the end of the 19th century, British attitudes began to change towards the drug, which is reflected in the literature of the period, including the likes of Charles Dickens, Oscar Wilde and Wilkie Collins. It tended to be associated with crime and with foreign immigrants, reflecting the social attitudes of Britain at the time.
Opium gives the user a dream-like high that heroin users claim is similar but cleaner than heroin. Marijuana users claim it has a similar but more intense high too. The high can last for several hours, depending upon the amount taken. It is an addictive drug, but as its use has been eclipsed by the popularity of heroin, it is not common to meet an opium addict in the Western world. As morphine and codeine are isolated from the opium poppy, (as well as heroin), opium is hugely important within the medical profession for producing pain killers. However, doctors agree that there is no alternative to opiates that have the same pain killing properties without the equal potential for addiction too.
As heroin is easier to smuggle, being less dense, pure opium is rare in the Western world. To many people it has a romantic and exotic image. So much so that there is a perfume named after it.
During the 1840s, British warships shelled several Chinese ports for the right to import opium from India to China. The Opium Wars again broke out in the late 1850s. These wars gave the English language the expression "gunboat diplomacy" and secured Hong Kong as a British colony until 1997. Indeed, the import and export of opium was crucial to the British economy until its prohibition in the early 20th century.
Opium can be injected, but most popularly smoked in pipes or chased on foil like heroin. Its use goes back to Ancient times and is mentioned in texts from the Babylonians, Phoenicians, Assyrians, Greeks, Egyptians and Romans and traded throughout the Mediterranean and known Ancient world.
Its use was also widespread throughout the Islamic world. This caused its stigmatization by the Spanish Inquisition as a non-Christian influence, and it fell from favour until Paracelsus developed laudanum in the 16th Century. Laudanum is a "tincture" of opium disolved in alcohol and used as a painkiller/anaesthetic. Laudanum was widely used in Victorian times-indeed the Queen herself is rumoured to have used it.
Opium has a wide and colourful history, but in modern times the majority of opium is mainly cultivated in the Indo-Chinese world, as well as Afghanistan and South East Asia. Opium poppies however, can be grown all over the world.
The most famous literary reference to opium is the classic "Confessions Of An English Opium Eater" by Thomas De Quincey. The poet Coleridge was a well known user, as was Alfred Lord Tennyson. Horatio Nelson is probably the most famous opium addict, which began when he was given it as a pain killer after his arm was amputated. Other notable addicts included anti-slavery campaigner William Wilberforce and Clive of India. Towards the end of the 19th century, British attitudes began to change towards the drug, which is reflected in the literature of the period, including the likes of Charles Dickens, Oscar Wilde and Wilkie Collins. It tended to be associated with crime and with foreign immigrants, reflecting the social attitudes of Britain at the time.
Opium gives the user a dream-like high that heroin users claim is similar but cleaner than heroin. Marijuana users claim it has a similar but more intense high too. The high can last for several hours, depending upon the amount taken. It is an addictive drug, but as its use has been eclipsed by the popularity of heroin, it is not common to meet an opium addict in the Western world. As morphine and codeine are isolated from the opium poppy, (as well as heroin), opium is hugely important within the medical profession for producing pain killers. However, doctors agree that there is no alternative to opiates that have the same pain killing properties without the equal potential for addiction too.
Cocaine and Crack (Coke/Charlie/Toot/Rock)
Cocaine used to be the "rich man's drug", fashionable in high society circles and among rock stars of the 1970's. During the 1990s and 21st century, cocaine has undergone a renaissance, particularly in the UK, where it has become a popular recreational drug. Like cannabis, it is used by people in every walk of life, regardless of income or class. Crack cocaine is essentially the same drug but crystalised with bicarbonate of soda and smoked in a glass pipe, sometimes improvised from lightbulbs. Freebase is another popular derivative-cocaine paste, known in South America as "paco"-pasta de cocaina. This is cocaine in the intermediate stages of the processing into powder and like crack, as it is a cheaper alternative to cocaine in its powder form, it is popular in poorer neighbourhoods. These forms of cocaine has a hit that lasts between five to ten minutes, followed by an extreme low due to the dopamine level in the brain dropping dramatically. This usually is followed by the user taking more.
The belief that crack is highly addictive is the subject of much debate. The health risks are high and the drug can cause psychological problems and intense paranoia, but the addictive nature of crack is more believed by doctors to be psychological, as many users go for days without using it. It is now believed to be linked more to the social context of the user.
Normal cocaine can be injected, taken orally (usually rubbed into the gums) and most commonly chopped into a line and "snorted"-inhaled up the nostrils, through a rolled up banknote.
Cocaine is thought of as a club drug, and also popular at parties. As incomes have increased, so has the demand for cocaine.
Like heroin, is is used medically as an anaesthetic, but while heroin is a depressant, cocaine acts as a stimulant on the central nervous system, causing a euphoric feeling that lasts approximately 15 minutes to half an hour. Users often experience a feeling of invulnerability, often to the point of arrogance. Many of the top Nazis were known to be cocaine users, and some historians have speculated that Hitler was high on cocaine when he decided to invade Russia. Though it is possible, there is no evidence for this, and Hitler was known to use drugs for medical reasons, rather than recreational.
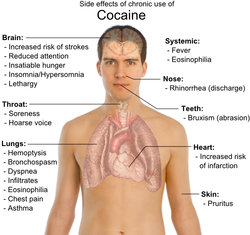
Another similarity between cocaine and heroin is the lack of purity. Cocaine is usually cut with glucose, but other impurities are added, such as novocain and other anaesthetics. Again, this causes all kinds of health risks, many which are illustrated in the picture opposite. Like heroin, it is virtually unheard of to find pure cocaine at street level, The average street cocaine is less than 50% pure.
Long term cocaine use results in the user taking it to keep them awake, rather than to get high. While cocaine is NOT physically addictive, it is incredibly addictive psychologically. Users are also at risk of overdosing, particularly as it tends to be a substance that is used at regular intervals throughout the evening, rather than just one hit to last for the night.
Cocaine comes from the coca plant-the former secret ingredient of coca-cola (hence the name), which is grown in South America, in Peru, Bolivia and particularly Colombia, where 45% of the world's cocaine comes from. The indigenous communities of these countries have always chewed the leaves of the coca plant, with no ill effect. However, the process that is used in the production of cocaine has changed little over the last hundred or so years, and this is anything but natural. It involves the coca leaves being dried, chopped to pieces then soaked in petrol with cement powder for a day. It is then pressed and battery acid is added, along with caustic soda. It is then filtered through cloth. Various other impurities are then thrown into the mix before it hits the streets in whatever form be it salt, crack or freebase.
Long term use of cocaine causes paranoia, depression and in some extreme cases, suicide. Physically, it can cause pulmonary and cardiac problems as well as the constant runny nose prevalant among users. Insomnia, restlessness and lethargy are also possible side effects. The user is also prone to bruxism, the involuntary grinding of the teeth, causing dental problems. People who use cocaine orally often have dental problems due to the high glucose content rubbed into the gums. It should be recognised, however, that for occasional users, the risks are lower than those of tobacco and alcohol, and is unlikely to result in social delinquency in the same way as some other drugs.
The belief that crack is highly addictive is the subject of much debate. The health risks are high and the drug can cause psychological problems and intense paranoia, but the addictive nature of crack is more believed by doctors to be psychological, as many users go for days without using it. It is now believed to be linked more to the social context of the user.
Normal cocaine can be injected, taken orally (usually rubbed into the gums) and most commonly chopped into a line and "snorted"-inhaled up the nostrils, through a rolled up banknote.
Cocaine is thought of as a club drug, and also popular at parties. As incomes have increased, so has the demand for cocaine.
Like heroin, is is used medically as an anaesthetic, but while heroin is a depressant, cocaine acts as a stimulant on the central nervous system, causing a euphoric feeling that lasts approximately 15 minutes to half an hour. Users often experience a feeling of invulnerability, often to the point of arrogance. Many of the top Nazis were known to be cocaine users, and some historians have speculated that Hitler was high on cocaine when he decided to invade Russia. Though it is possible, there is no evidence for this, and Hitler was known to use drugs for medical reasons, rather than recreational.
Another similarity between cocaine and heroin is the lack of purity. Cocaine is usually cut with glucose, but other impurities are added, such as novocain and other anaesthetics. Again, this causes all kinds of health risks, many which are illustrated in the picture opposite. Like heroin, it is virtually unheard of to find pure cocaine at street level, The average street cocaine is less than 50% pure.
Long term cocaine use results in the user taking it to keep them awake, rather than to get high. While cocaine is NOT physically addictive, it is incredibly addictive psychologically. Users are also at risk of overdosing, particularly as it tends to be a substance that is used at regular intervals throughout the evening, rather than just one hit to last for the night.
Cocaine comes from the coca plant-the former secret ingredient of coca-cola (hence the name), which is grown in South America, in Peru, Bolivia and particularly Colombia, where 45% of the world's cocaine comes from. The indigenous communities of these countries have always chewed the leaves of the coca plant, with no ill effect. However, the process that is used in the production of cocaine has changed little over the last hundred or so years, and this is anything but natural. It involves the coca leaves being dried, chopped to pieces then soaked in petrol with cement powder for a day. It is then pressed and battery acid is added, along with caustic soda. It is then filtered through cloth. Various other impurities are then thrown into the mix before it hits the streets in whatever form be it salt, crack or freebase.
Long term use of cocaine causes paranoia, depression and in some extreme cases, suicide. Physically, it can cause pulmonary and cardiac problems as well as the constant runny nose prevalant among users. Insomnia, restlessness and lethargy are also possible side effects. The user is also prone to bruxism, the involuntary grinding of the teeth, causing dental problems. People who use cocaine orally often have dental problems due to the high glucose content rubbed into the gums. It should be recognised, however, that for occasional users, the risks are lower than those of tobacco and alcohol, and is unlikely to result in social delinquency in the same way as some other drugs.